Often rotator cuff injuries are associated with professional athletes, such as pitchers⚾️ and tennis players?. However, a majority of patients are those ages 50 and over. These individuals tend to be active and healthy, but over time injuries degenerate the rotator cuff?♀️?️?♀️. In worse cases, they may slip and fall, causing a traumatic tear.
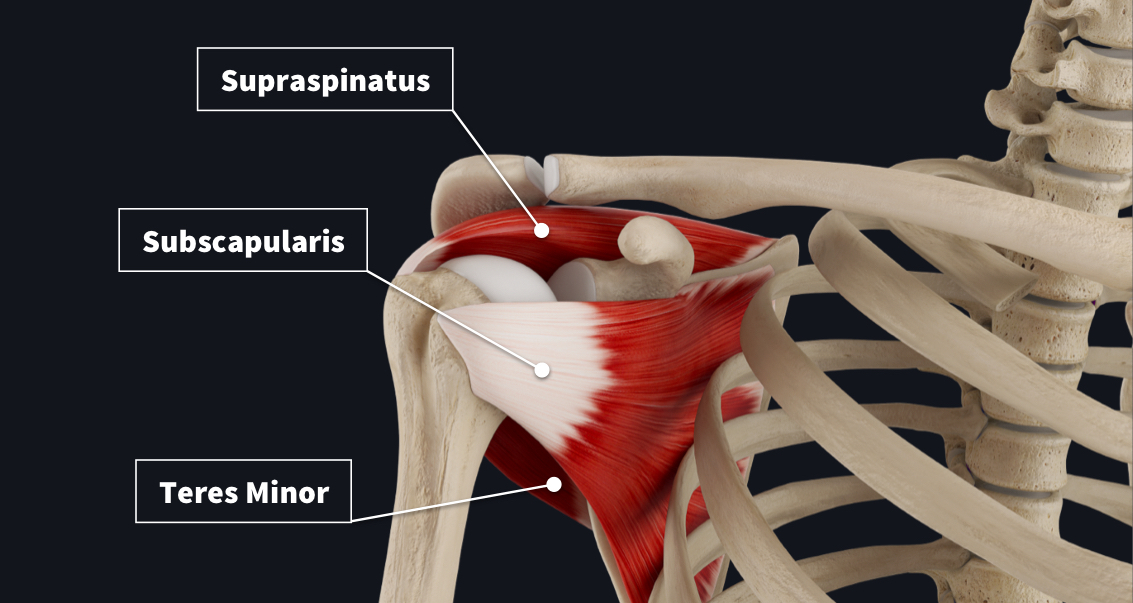
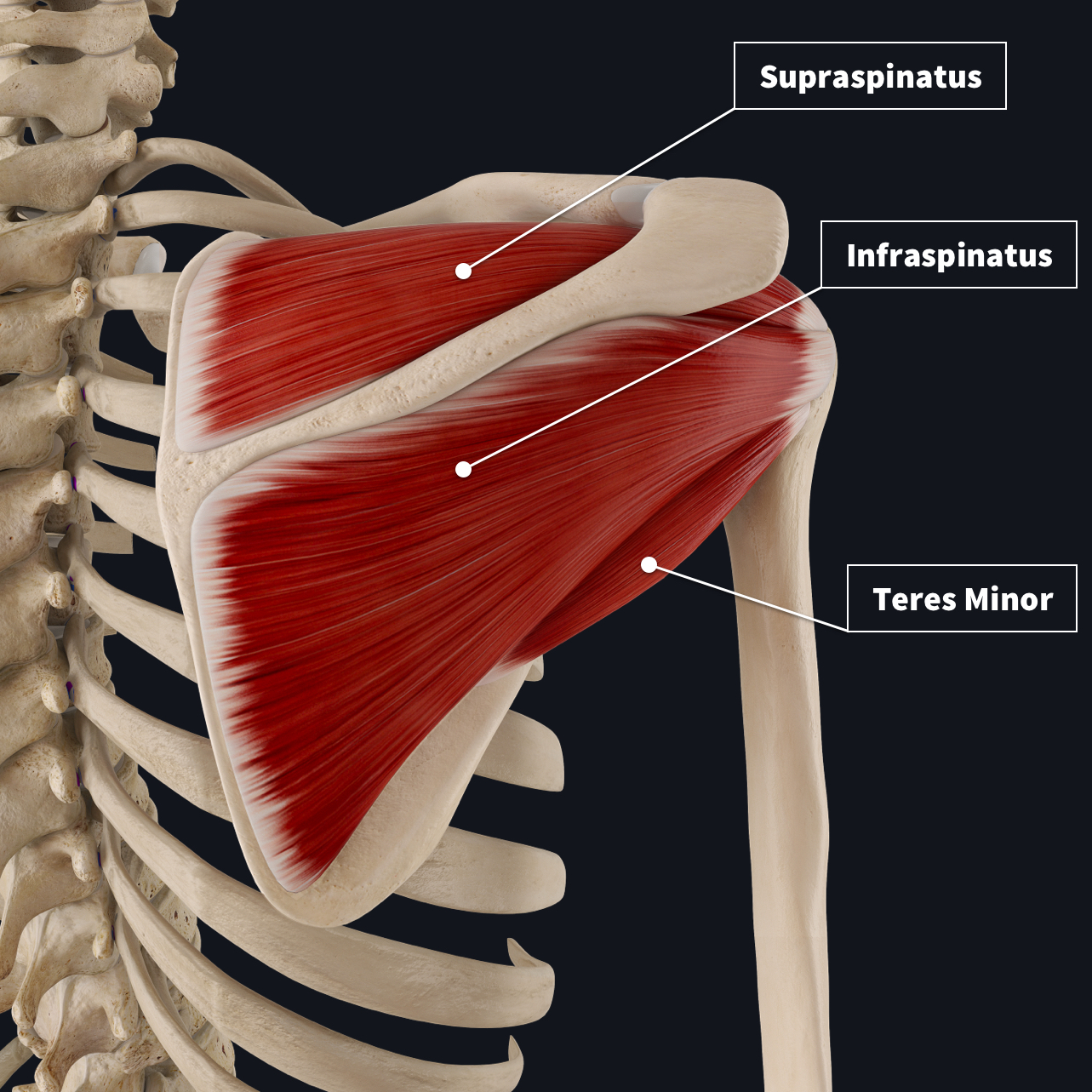
The rotator cuff muscles consist of four muscles that originate from the scapula and insert into the humeral head. Together, the resting tone of the muscles acts to pull the humeral head into the glenoid fossa, giving it stability.
You can use the crafty mnemonic “SITS” to remember these muscles
Supraspinatus
Origin & Insertion: Originates from supraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Innervation: Suprascapular nerve.
Actions: Abducts the arm and assists the deltoid.
Infraspinatus
Origin & Insertion: Originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Innervation: Suprascapular nerve.
Actions: Laterally rotates the arm.
Teres Minor
Origin & Insertion- Originates from the posterior surface of the scapula, next to its lateral border. Inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Innervation: Axillary nerve.
Actions: Laterally rotates the arm.
Subscapularis
Origin & Insertion- Originates from the subscapular fossa on the costal surface of the scapula. Inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus.
Innervation: Upper and lower subscapular nerves.
Actions: Medially rotates the arm.
Small injuries to this group of muscles can be treated with rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory painkillers if recommended by a doctor ?⚕️⚕️. However, surgery may be needed when all other treatments have failed?. Maintaining strength and flexibility in your shoulder can help prevent rotator cuff injuries??️.
Visually demonstrate in 3D what structures of a region are affected by a sports injury, and go deeper to better explain the physiology behind the musculoskeletal system with our range of microanatomy models. To see how Complete Anatomy can increase compliance through better patient education, try it for FREE today.
