March marks Brain Injury Awareness Month. Let’s explore one of the more common types of brain injury, a concussion. A concussion is classified as a mild traumatic brain injury.
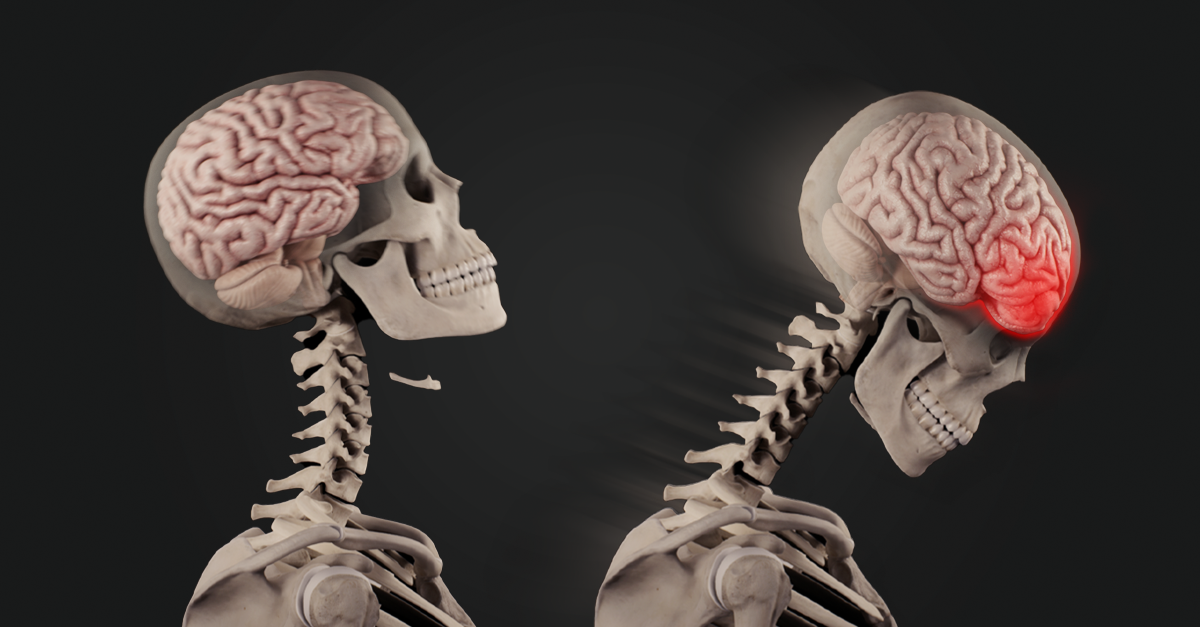
A concussion may be caused by a large impact or trauma to the head. Concussions can also be caused by rapid acceleration and deceleration of the head, such as in whiplash. Concussions are common in contact sports such as rugby and football. Other causes of concussions could be a fall, a bike accident or a car crash.
Due to the impact on the head, the brain slides around within the skull. This movement of the brain against the skull can temporarily injure the brain and affect its functionality.
Common symptoms of a concussion include a headache, ringing ears, blurry vision, nausea, fatigue, confusion and amnesia. Onlookers may observe someone with a concussion to have loss of consciousness, slurred speech, confusion, forgetfulness and delayed responses.
The effects of a concussion are usually short-term, only lasting for a couple days or weeks. Most people fully recover after a concussion, with no lasting effects. However, sometimes there can be further complications from a concussion. For example, a recently concussed person can experience post-traumatic headaches or vertigo.
Treatment for a concussion includes rest, avoiding stress, avoiding screen time and icing the area of impact. It is important to have the proper rest after experiencing a concussion. For instance, if the concussion was due to playing sports, the person should wait until they are fully recovered before returning to the sport. There is a rare chance of second impact syndrome in which there may be rapid brain swelling and even death if a person receives a second concussion before fully recovered from the first.
Share this post to spread awareness of brain injuries this month!
