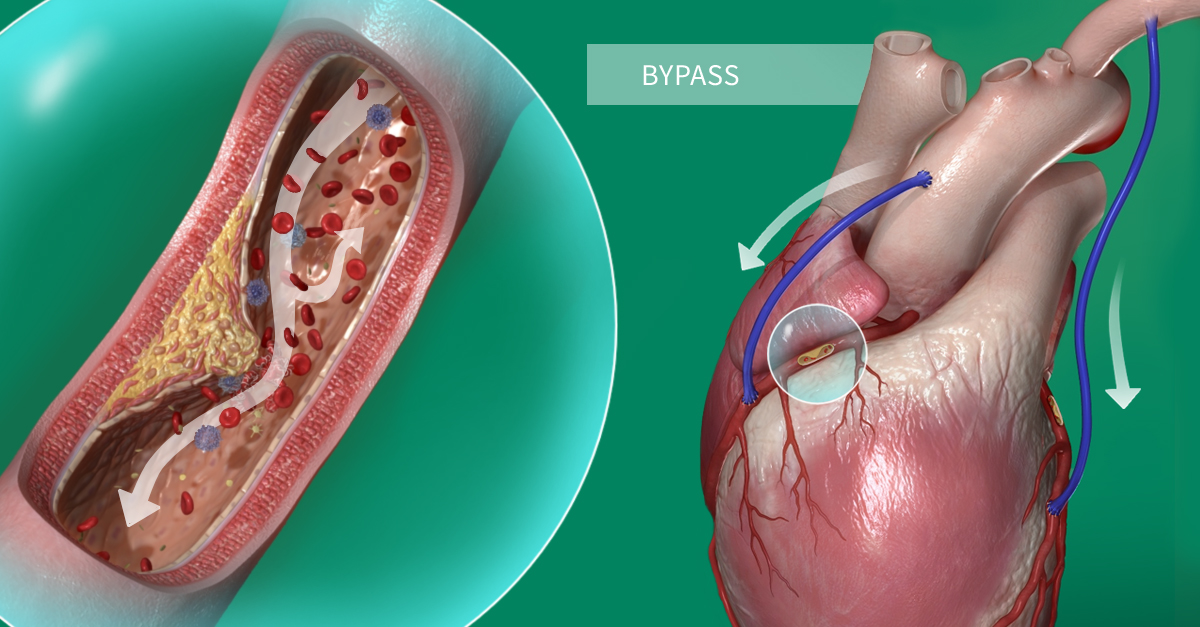
A coronary artery bypass or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary heart disease. When the major arteries become clogged by fatty substances, a CABG diverts blood flow around the congested parts and aids in oxygen supply to the heart. It is estimated that around 200 million people in the world are living with coronary heart disease. In 2019 it was the world’s leading cause of death globally.
The procedure of a CABG is straight forward. It involves taking a blood vessel from an area of the body such as the chest, leg, or arm. The blood vessel is then attached to the coronary artery from above and below the area that is blocked/narrowed with the fatty substance. The new blood vessel is referred to as the bypass graft. You can have more than one bypass graft depending on how severe the coronary heart disease is and how many of the coronary blood vessels are narrowed. The patient will be anesthetized and in general it takes around 3 to 6 hours to complete.
As a result, from this procedure a patient should experience an improvement in their breathlessness and chest pain. It is important to note that a CABG is not a cure for coronary heart disease. Other lifestyle changes are needed in order to help the condition such as eating healthy and getting exercise. In some cases, the procedure may need to be performed again and could require the help of a stent to open the arteries further, this is known as an angioplasty.
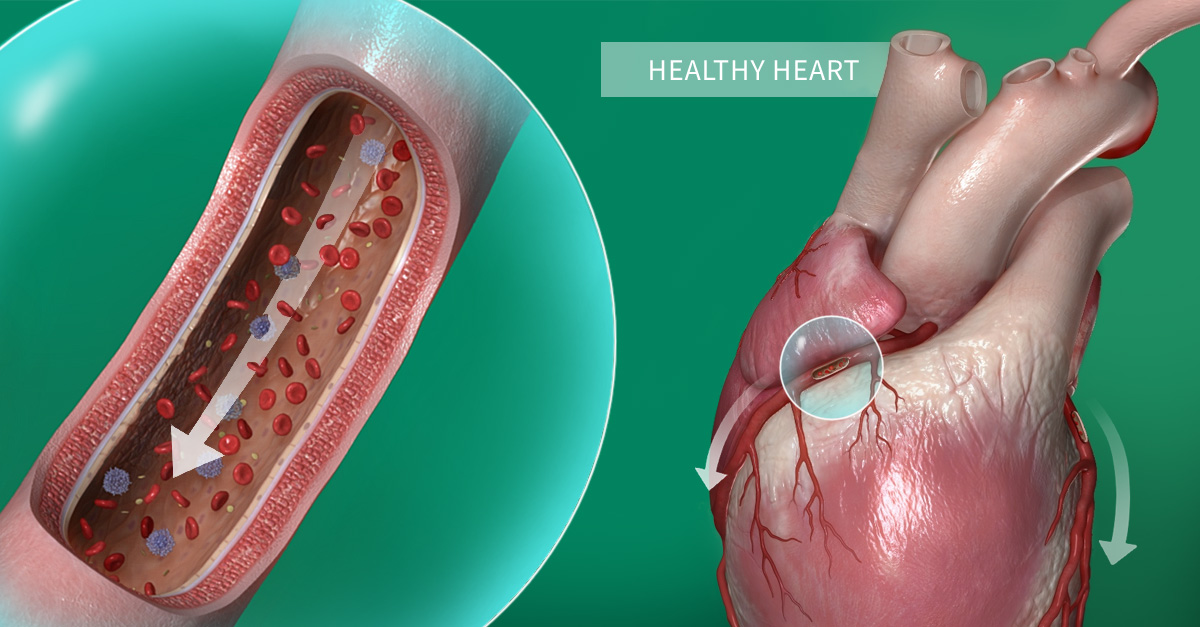
Our hearts receive blood from both the left and right coronary arteries. Avoiding conditions like coronary heart disease is very important to prevent the buildup of plaques (atherosclerosis) in these important vessels. Factors that can put one at risk are smoking, obesity, and a high-fat diet. If one of the plaques were to cause the coronary artery to rupture, a blood clot would form and block the blood flow to the heart. This would then result in a heart attack or myocardial infarction.
The CABG procedure is the most common cardiac procedure performed today in the United States, taking place around 200,000 to 300,000 times a year. Of these procedures, 25-30% are performed on women. The mortality rate for a CABG performed on a female, albeit low, is still higher than in males coming at 2.8% vs 1.7% in men. This difference highlights the importance in female health and considering its unique anatomy and physiology from that of its male counterpart when performing surgery. Some of the factors that may be connected to this are that women tend to be 3-5 years older than men who undergo CABG. Women also present symptoms differently than men. Lastly, fewer than 20% of patients in clinical trials have been female.
