Happy World Immunisation Week! Here’s a special Anatomy Snippet on osteo-immunity ?
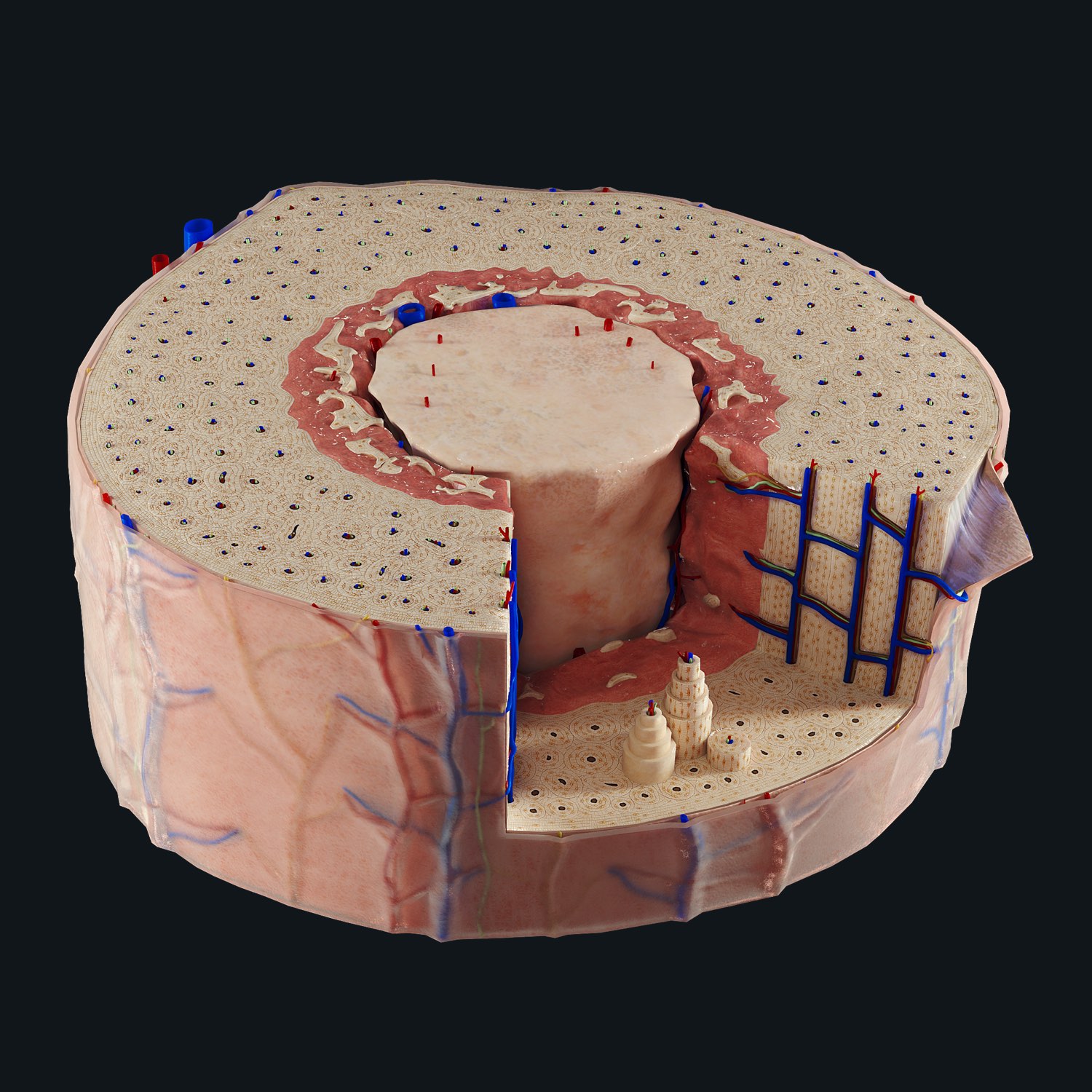
The skeletal system is composed of individual bones (pictured: cross-section of the human bone), each bone is a complex organ composed of numerous groups of cells which have multiple functions. Some of these functions include: providing structural support to the body, allowing for precise controlled movement of the body around joints (with the help of muscles), and being the site of hematopoiesis, a.k.a. blood cell development.
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism, providing us with protection against invading pathogens. Osteo-immunity describes the relationship between the skeletal system and the immune system, and how they are both made up of complex tissues which can often interact in their functions. The interactions between the cells of the skeletal and the immune system are now well documented:
- Bone marrow found within the interior walls of bones is crucial for the proper development of the immune system, in addition to this it houses stem cells used in maintenance of the immune system.
- The regulation of bone by hematopoietic and immune cells.
- The immune system produces cytokines which are involved in the regulation of bone homeostasis.
- Cells related to osteoblasts, a type of bone cell, have been shown to regulate the production of blood cells – which are primary components of the immune system.
Both systems work together to bring effective immunity to the body, developing the best line of defense against dangerous pathogens. Further research into the interactions between these systems hopes to result in better therapeutics for conditions affecting one or both of these systems.
