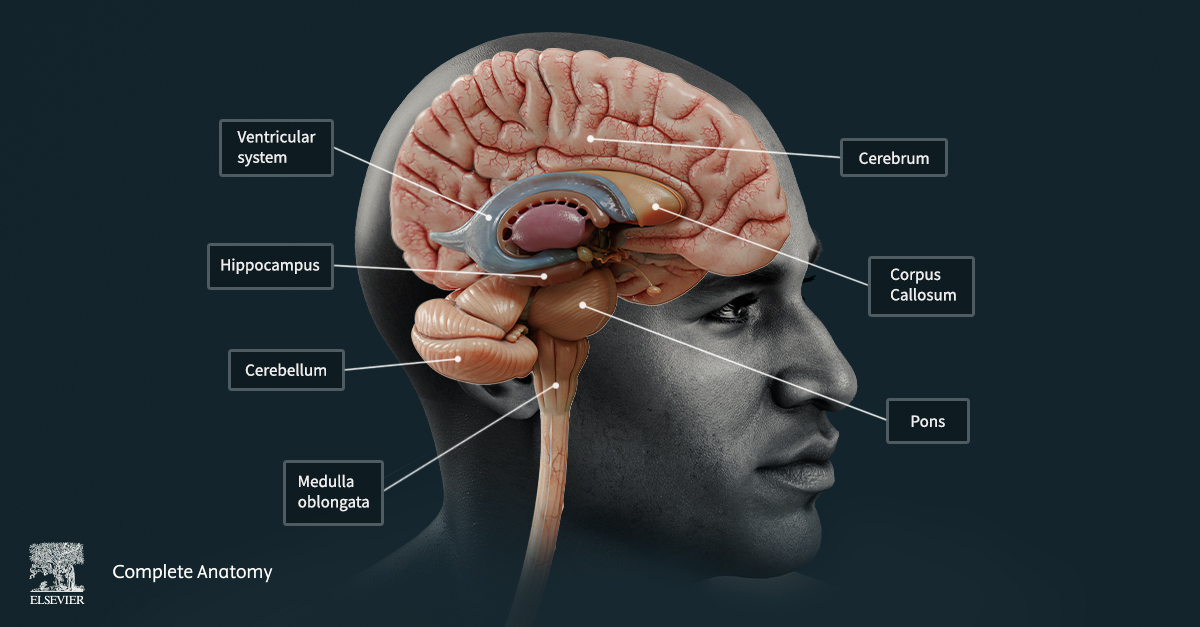
A great way to understand what Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia are, is to first understand the basic anatomy of the brain.
The brain can be simplified into key structures. The cerebrum is the bulk of the brain. It can be divided into the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes as well as the limbic lobe and insula. The cerebrum is composed of white and grey matter. Grey matter is the outer surface of the cerebrum and consists of the cell bodies and dendrites of neurons. Grey matter is important for processing information and cognition. White matter is the inner part of the cerebrum and consists of the axons of the neurons. White matter is important for communicating between different areas of the brain, and between the brain and the rest of the body. For example, the corpus callosum is a white matter structure that communicates between the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
There are many structures found within the cerebrum. Fitted around these structures are a series of chambers collectively known as the ventricular system. The ventricular system contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which aids in shock absorption, waste removal and nourishment.
Connecting the brain to the spinal cord in the brainstem. The brainstem can be divided, from superior to inferior, into the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata. It is where the majority of the cranial nerves emerge from. The brainstem regulates many vital functions such as breathing, balance, facial movements and heart rate. Connected to the brainstem is the cerebellum, or “little brain”. The cerebellum has roles in the control and learning of movement.
Dementia is a term that describes a condition of the brain that causes issues with memory and cognition that severely affect daily life. The most common form of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease causes loss of neurons and tissue throughout the entire brain, with initial damage found in the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus. These parts of the brain both have important functions in memory.
Check out Complete Anatomy to further understand the anatomy of the brain!
